The following report was created in partnership with Bellingcat. The Arabic version of this report can be read here.
Preface: On February 1st, 2018 Duma city[1] was shelled with poisonous gases for the third consecutive time in less than one month, and according to many testimonies STJ obtained through its network of field reporters and Bellingcat’s analysis of open source material, five rockets, loaded with chemical substances believed to be chlorine gas, landed in the densely populated area in the western neighborhoods of Duma, resulting in the suffocation of three civilians, including a woman.
Syrian regular forces had twice previously used poisonous gases on Eastern Ghouta. The first time was on January 13, 2018, where the area that links Harasta and Duma cities was shelled with poisonous gases causing injuries to six civilians, including women and children, examined in an earlier report STJ published. The second incident[2] occurred on January 22, 2018, where residential neighborhoods in the western northern region of Duma were shelled with poisonous gas resulting in the injury of 21 civilians, including women and children. STJ published a joint report with Bellingcat concerning that incident.
Analysing the used munitions in the attack:
According to Bellingcat, the munitions used in the February 1 attack are Improvised Rocket Assisted Munitions (IRAMs), based on modified Iranian 107mm rockets. The standard warhead has been replaced with a large pressurized gas cylinder, and tail fins have been added to the rocket. The munition matches exactly with the design of munition used in the January 22 2018 chlorine attack in Douma, Damascus, as well as chlorine attacks that took place in Damascus in early 2017. In some cases, rockets from the 2018 attacks share the same lot numbers, indicating they are from the same manufacturing batch. This strongly indicates that the rockets used in the 2018 attacks would have originated from the same source:

Top – Rocket markings from January 22, 2018 (source).
Bottom – Rocket markings from February 1, 2018 (source).
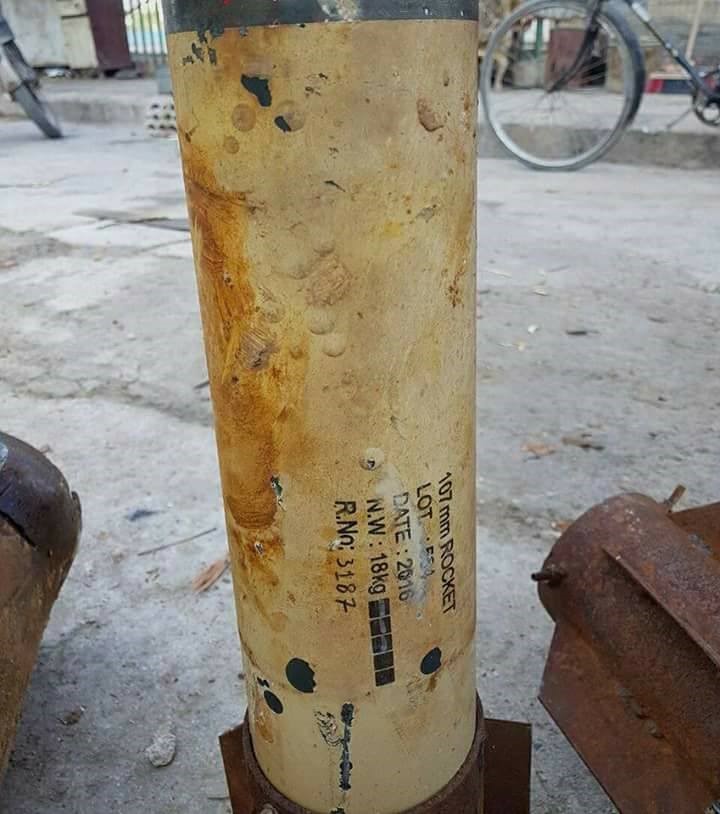

Remnants of the munitions used in the February 1, 2018 attack.
Photo credit: coordination of Duma.
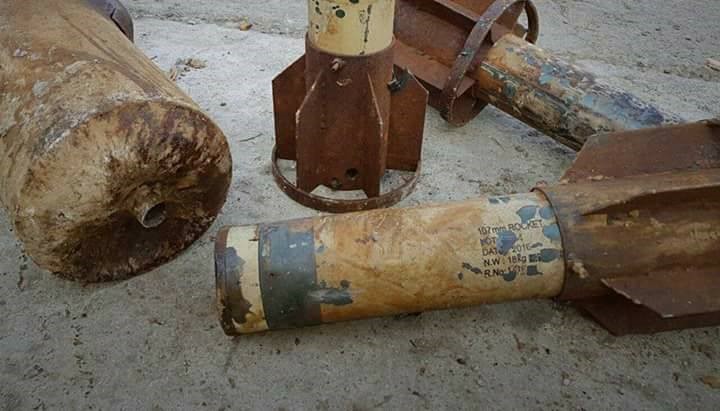

Image of the remnants of the rockets loaded with poisonous gases thrown on Duma in the "third attack" on February 1, 2018.
Photo credit: coordination of Duma.
Hasan al-Durra, from Duma, was at the site of the attack, and spoke to STJ:
"At 5:30 a.m. February 1, 2018, and while we, I and my family, were sleeping at home, we heard shooting of several rockets but we did not hear its explosion sound, and after a few minutes, we smelled home chlorine-like adore, it spread gradually until it became unbearable, and when we tried to get out of the house, the smell was stronger outside, so we went inside again, and I lit one of the heaters to keep the poisonous gas out, but we could still breathe well. I was so afraid for my children, and I didn’t know what to do, so then I brought pieces of wet cloth and put them on their faces, we stayed struggling to live until the sun came out and the odor began to fade gradually. "
Impact site and the source of the rockets:
Using videos posted by Firas Abdullah on the day of the attack it is possible to geolocate the impact sites of three of the rockets used in the February 1 attack to farmlands on the west side of Douma:
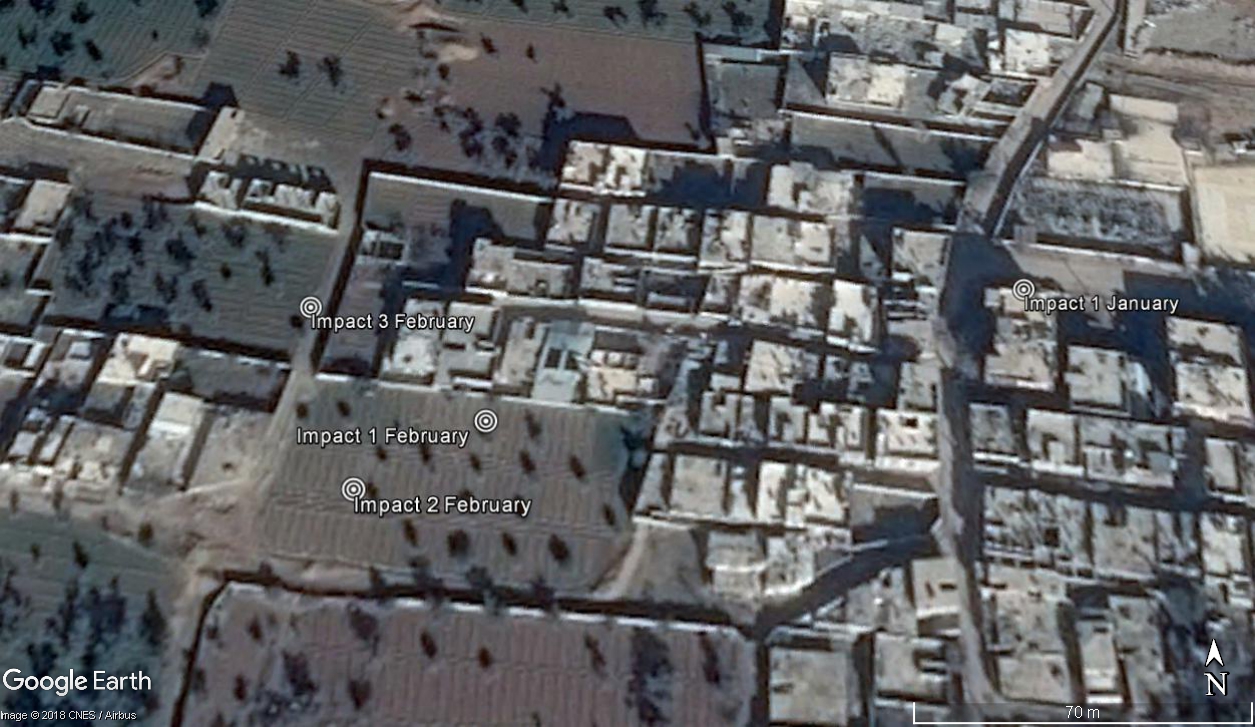

Impact sites of the 3 of the munitions used in the February 1 attack, geolocated and verified by witnesses
Image credit – Digital Globe/Google Earth
Multiple organisations and individuals have tracked the progress of fighting in the area on a regular basis, showing little movement in the front lines closest to the locations attacked, despite a recent attempt by government forces to capture the area. A map from pro-government "war correspondent, photographer and war map designer" Maxim Mansour posted on January 12, 2018, the day before another chlorine attack reported on January 13, shows government forces attacking the area:
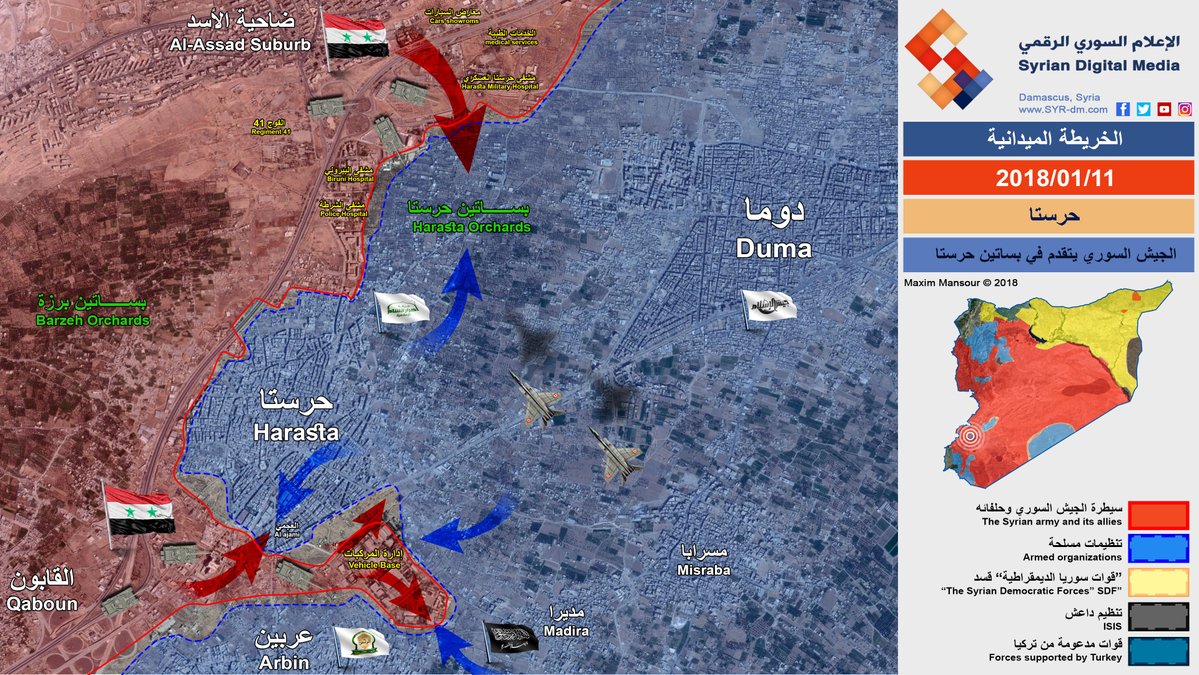
Maxim Mansour’s map showing frontlines in East Ghouta. Image credit – Maxim Mansour
Maps from the pro-government South Front website dated January 18 and January 29 show similar front line positions, with no change between the two dates. Maps from the pro-opposition FSA News also show the same front lines during that period, as does the conflict mapping website LiveUAMap. With this agreement among multiple sources about the position of front line positions the closest government positions to the impact sites would be 400-600m away.
It is also possible to establish the likely trajectory of rockets used in the February 1 attack. In one geolocated video, Firas Abdullah films the impact crater of one of the rockets:

The crater from the impact of one of the munitions used on February 1 2018
Image credit – Firas Abdullah
The shape of this crater indicates the rocket would have come from the west, from the direction of the Syrian government positions around 1km away. In another video filmed by Firas Abdullah, we see an impact site where the warhead of the chemical munition is still embedded in the ground, close to a large wall. The impact crater is west of the wall, which runs north-south, and the height of the wall, and the position of the impact crater, would make it extremely unlikely for the munition to have come from the east without first hitting the wall. This again indicates the munition would have come from government positions in the west. Further to the west, the 41st Regiment military base can be found 2km away from the impact sites.
In another testimony by a paramedic rushed to the scene of the attack, he told STJ that five rockets loaded with poisonous gas had fallen near the area of the Local Stadium in Duma, which is one of the populated areas, and in that regard, he continued:
"The smell was very strong, so we started to help the injured as there were four cases transferred to Damascus Countryside Specialty Hospital. Five Katyusha rockets (modified rockets) with homemade devices fired into the same area, and most of them exploded immediately after they hit the ground, I could see those five rockets with their containers while we were checking civilians safety in the area. Anyway, the distance was not so great between the locations of those rockets not more than 30 m maximum, and I could see a green substance trun to blue on the rocket detonator similar to the substance on the frames of the containers, I didn't know what it was, but all I knew was that these rockets caused significant casualties among civilians in large areas within populated neighborhoods reaching 3 km depth within Duma, that matter caused a state of intense panic and fear among people.”

Image a filling valve attached to the front of one of the warheads. Photo credit: STJ
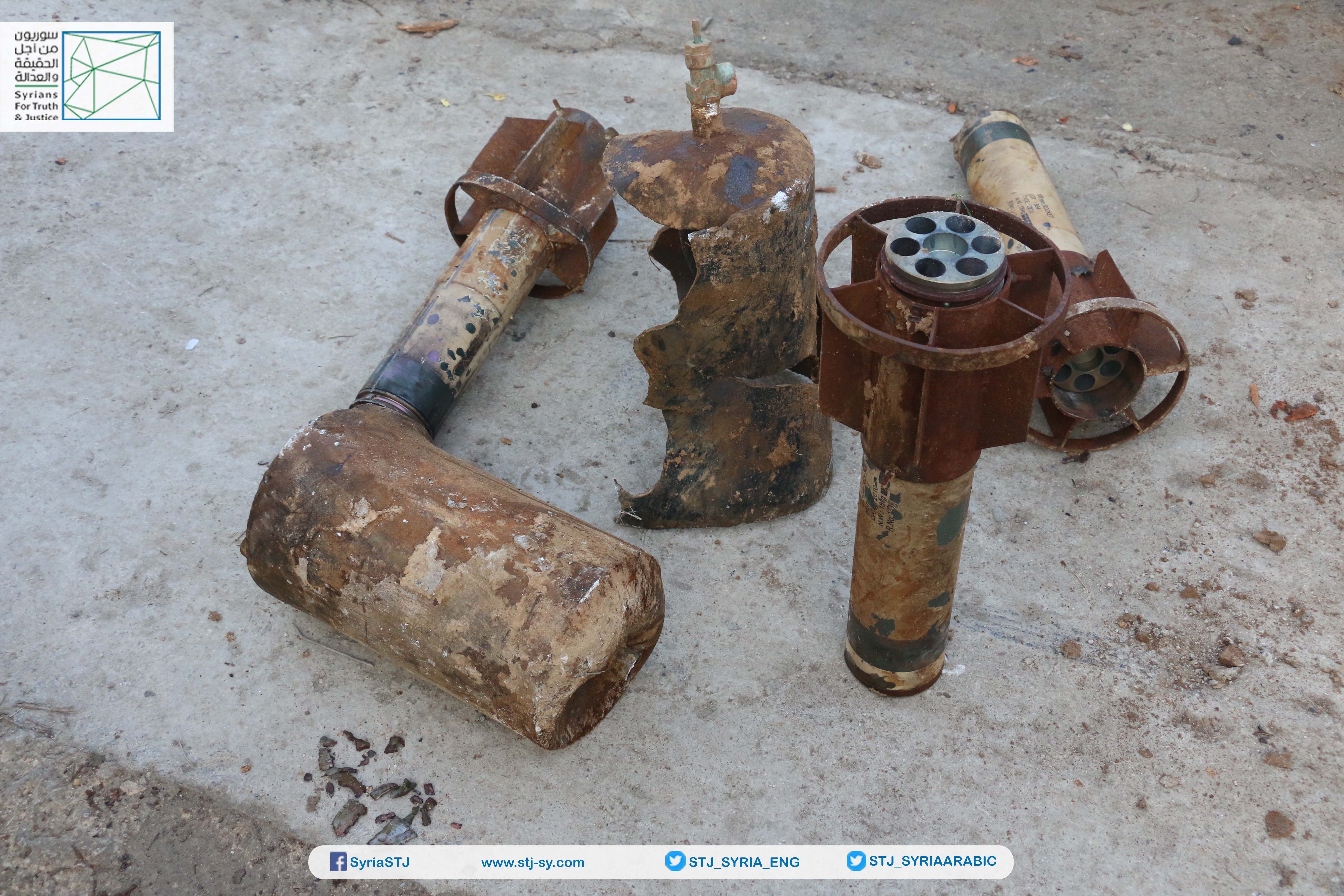

Image shows three rocket motors, and two warheads, from the munitions used in February 1, 2018 attack. Photo credit: STJ
Yasser Al-Shami, the director of the medical office in Duma, told STJ that many cases had been transferred to the medical centers in the city. However, early warning and rapid evacuation of civilians contributed to reducing the number of casualties, he continued:
At 5:45 a.m. February 1, 2018, we received three cases of toxic gas inhalation, including women, suffering from dyspnea, irritation and sweating in spite of the cold weather. It was clear from the smell of their clothes that they were exposed to a gas attack similar to chlorine smell. These cases were treated by sprays and bronchodilator, and stayed under medical observation for two hours and then we released them. "
On February 2, 2018, the local council of Duma published a statement confirming that at 5:30 AM the residential neighborhoods of Duma. had been exposed to attack by poisonous gas using ground-to-ground missiles, which caused injuries among civilians, the statement also pointed out that this attack was the third attack of its kind in less than a month.

The statement issued by the local council of Duma on February 1, 2018. Photo credit: The local council of Duma.
Several sources told STJ that the rockets launched at Duma had been fired from the Regiment (41) base adjacent to the area of Barzeh. They also stated that the poisonous gas had reached many neighborhoods of the city, causing panic in the local population, as locals thought that the used gas was chlorine. Activists stated they believed it was very likely that Syrian forces had modified this gas to produce future effects and more severe damage than usual for usual chlorine gas.
Video footage published by Smart Agency on February 1, 2018 showed remnants of the munitions used in the attack noting that the Syrian regular forces had used ground-to-ground rockets loaded with poisonous gas on the outskirts of the city.
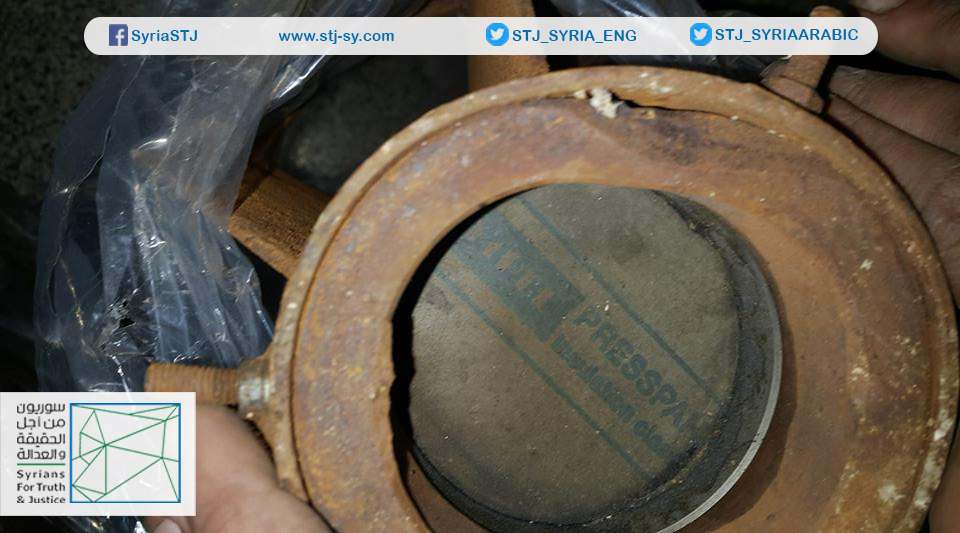
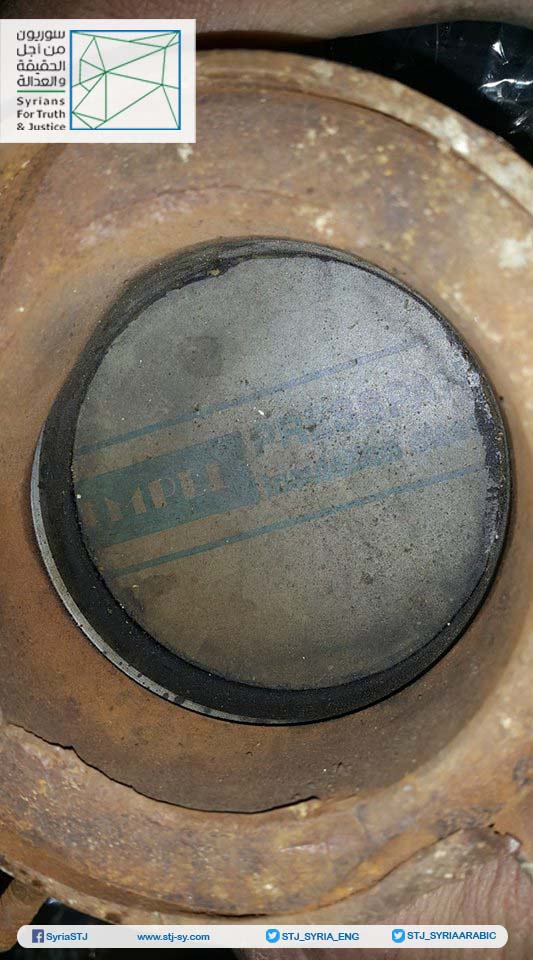
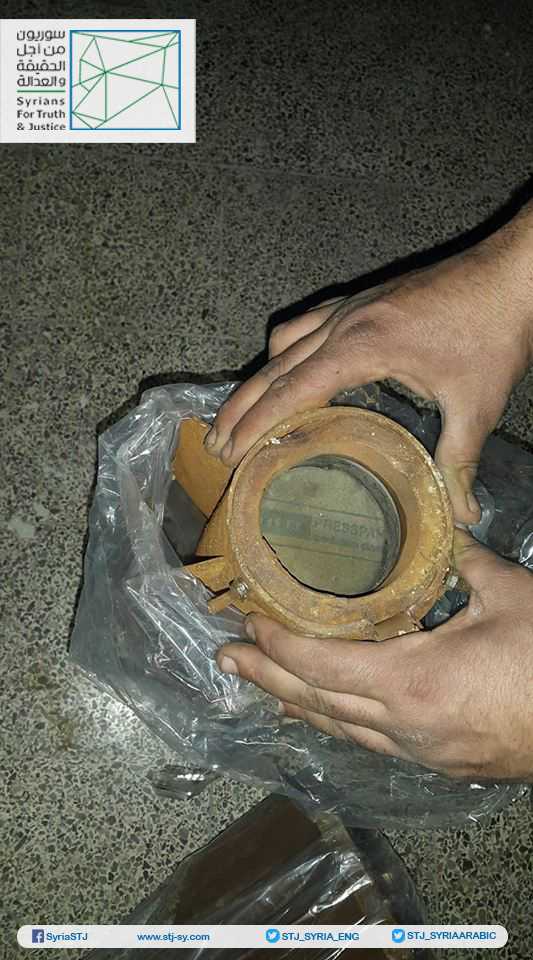
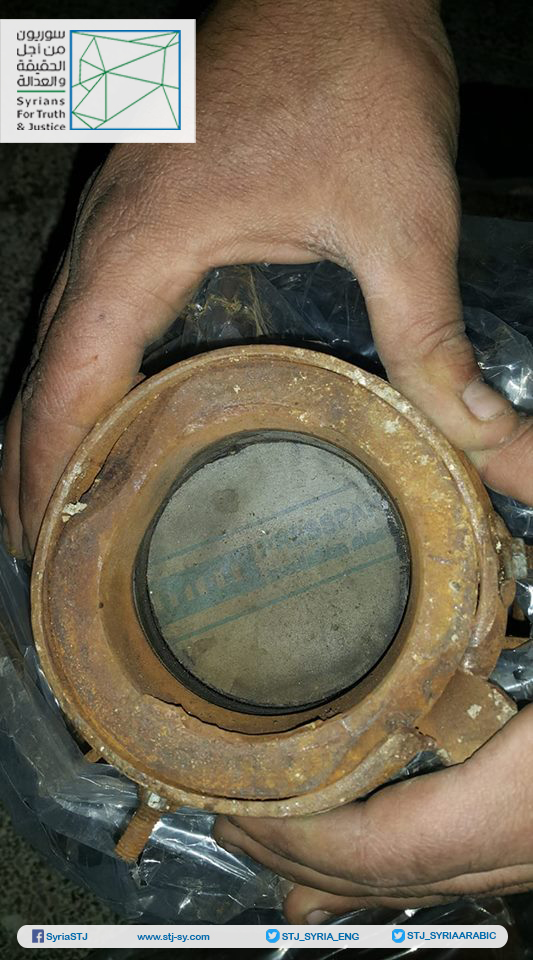
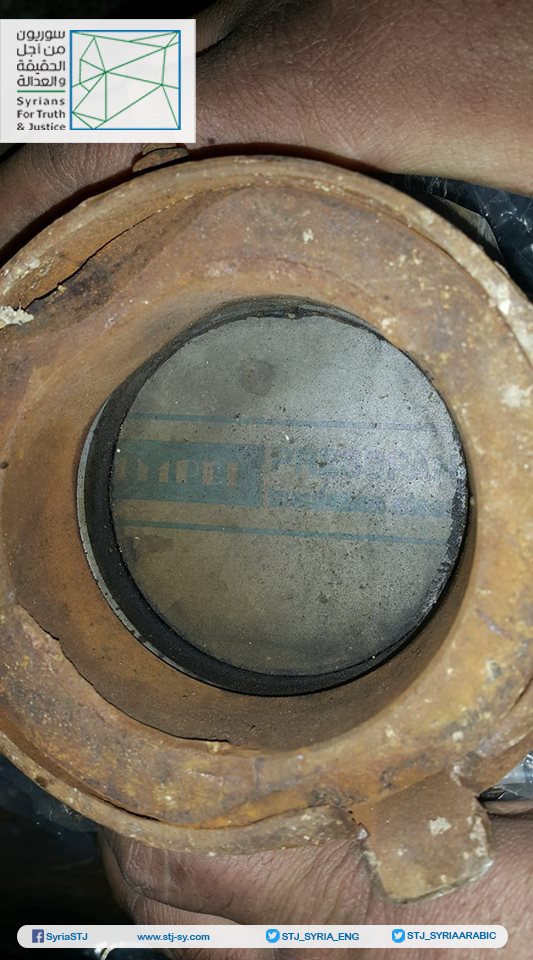
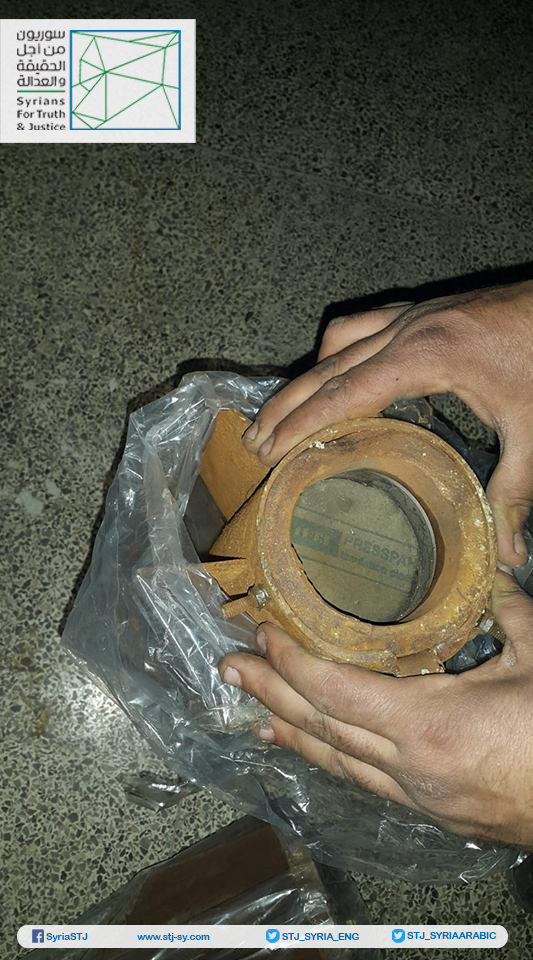
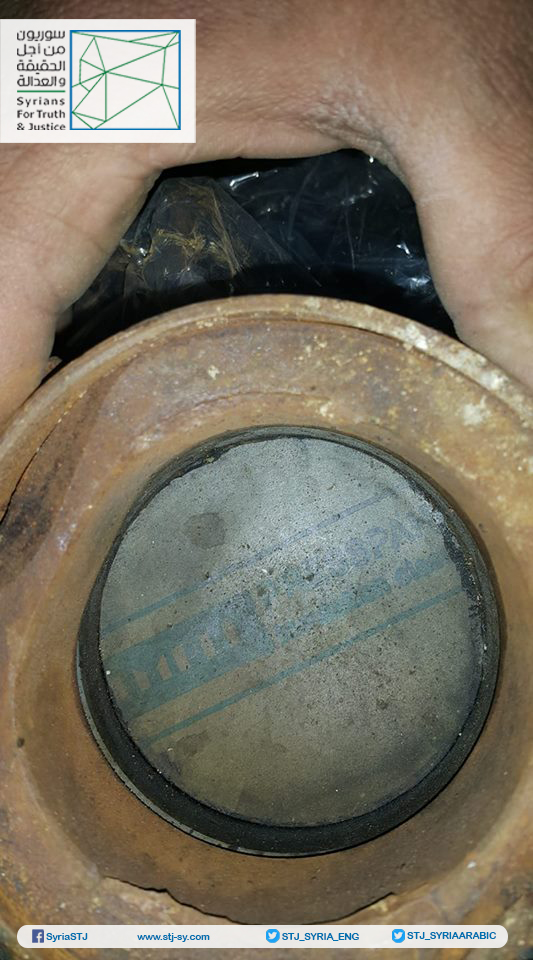
Annex: Images taken by Syrians for Truth and Justice showing the German insulation material inside one of the rockets that had been used in the third chemical attack in Eastern Ghouta on February 1, 2018.








[1] Duma is under the control of Army of Islam.
[2]This attack comes in the context of the military campaign launched by the Syrian regular forces on Eastern Ghouta on November 15, 2017, following the announcement of Ahrar al-Sham al-Islamiyya Movement the battle "They Were Wronged", which began in two stages. The first stage began on November 14, 2017, when the battles resulted in the death of several soldiers of the Syrian regular forces alongside the control of Ahrar al-Sham al-Islamiyya Movement on large parts of the Military Management Vehicles in Harasta. The second phase began on December 29, 2017, when battles imposed a siege on the Military Management Vehicles by Ahrar al-Sham al-Islamiyya Movement, in addition to controlling both the Al-Ajami neighborhood, the automatic oven and al-Hadaeq neighborhood that stretches along the road between Harasta and Arbin from the west side of the Military Management Vehicles. The third stage began on January 28, 2018, when the al-Sham al-Islamiyya Movement detonated a tunnel for the regular forces within Military Management Vehicles in Harasta, which resulted in the death and injury of a number of Syrian regular forces.

